Oct 12, 2015
Apr 28, 2011
Hydrogen Bonding
What is hydrogen bonding?
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, that comes from another molecule or chemical group. The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond. These bonds can occur between molecules (intermolecularly), or within different parts of a single molecule (intramolecularly).
Intermolecular hydrogen bonding:
Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is seen in water molecule as a result of interaction between the oxygen and hydrogen atom of water molecule. Since oxygen is somewhat electronegative, it acquires electrons of both hydrogen atom towards itself and thus the oxygen atom seem to have negative charge while hydrogen with positive.The hydrogen bond is the result of interaction between these two charges.
 |
| Intermolecular Hydrogen bonding in water molecules |
In the above fig. the dotted lines represents the Hydrogen bond between water molecules.
Apr 14, 2011
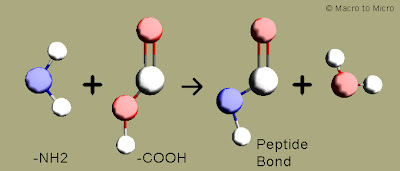
Peptide bond says "Proteins from aminoacids"
Proteins are the body building materials of most of the organisms.Proteins are otherwise known as polymers of aminoacids.Two aminoacid is bonded through a peptide bond to form a peptide.Further these peptides are connected to form polypeptides, which on combination forms proteins.
Peptide bond:
The -NH2 group of one aminoacid makes a bond with -COOH of another aminoacid by giving out a water molecule to form -CONH.This is known as peptide bond.
Peptide bond:
The -NH2 group of one aminoacid makes a bond with -COOH of another aminoacid by giving out a water molecule to form -CONH.This is known as peptide bond.
Apr 12, 2011
E=mc^2 - Is it right?
The equation E=mc^2, given by Albert Einstein is the most significant one in the atomic level which paved the way for nuclear reactors, the future energy source to human being.Many people doubt this equation, but it can be solved by simple dimensional analysis.
Dimensional analysis is the simplest way to analyze whether the equation is dimensionally correct or not.
Basically it is based on three dimensions, namely mass(M), length(L), and time(T).
Dimensional analysis of E=mc^2 :
Let 'E' be the ..........L.H.S &
mc^2 be the ............R.H.S
'E' refers to energy, which has the dimension of Force multiplied by displacement.According to newton, F=ma,
Dimensional analysis is the simplest way to analyze whether the equation is dimensionally correct or not.
Basically it is based on three dimensions, namely mass(M), length(L), and time(T).
Dimensional analysis of E=mc^2 :
Let 'E' be the ..........L.H.S &
mc^2 be the ............R.H.S
'E' refers to energy, which has the dimension of Force multiplied by displacement.According to newton, F=ma,
Apr 8, 2011
Aminoacid 2 - Arginine
Arginine is also an α-amino acid.
Properties:
Molecular Formula :- C6H14N4O2
Molar mass :- 174.2 g mol−1
Structures:
The amino acid side chain of arginine consists of a 3-carbon aliphatic straight chain, the distal end of which is capped by a complex guanidinium group.With a pKa of 12.48, the guanidinium group is positively charged in neutral, acidic and even most basic environments, and thus imparts basic chemical properties to arginine. Because of the conjugation between the double bond and the nitrogen lone pairs, the positive charge is delocalized, enabling the formation of multiple H-bonds.
3D structures:
Properties:
Molecular Formula :- C6H14N4O2
Molar mass :- 174.2 g mol−1
Structures:
The amino acid side chain of arginine consists of a 3-carbon aliphatic straight chain, the distal end of which is capped by a complex guanidinium group.With a pKa of 12.48, the guanidinium group is positively charged in neutral, acidic and even most basic environments, and thus imparts basic chemical properties to arginine. Because of the conjugation between the double bond and the nitrogen lone pairs, the positive charge is delocalized, enabling the formation of multiple H-bonds.
3D structures:
Apr 7, 2011
Aminoacid 1 - Alanine
Alanine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula CH3CH(NH2)COOH. Alpha α-carbon refers to the carbon directly bonded to the functional group.Here the carbon attached to the -COOH carboxylic group is called as Alpha carbon and hence it is named as alpha amino acid. It is classified as a nonpolar amino acid. D-Alanine occurs in bacterial cell walls and in some peptide antibiotics.
Properties:
Molecular Formula :- C3H7NO2
Molar mass :- 89.09 g mol−1
Appearance :- White powder
Solubility :- Soluble in water
Melting point :- 258 ºC
Structure:
The α-carbon atom of alanine is bound with a methyl group (-CH3), making it one of the simplest α-amino acids with respect to molecular structure and also resulting in alanine's being classified as an aliphatic amino acid. The methyl group of alanine is non-reactive and is thus almost never directly involved in protein function.
Properties:
Molecular Formula :- C3H7NO2
Molar mass :- 89.09 g mol−1
Appearance :- White powder
Solubility :- Soluble in water
Melting point :- 258 ºC
Structure:
The α-carbon atom of alanine is bound with a methyl group (-CH3), making it one of the simplest α-amino acids with respect to molecular structure and also resulting in alanine's being classified as an aliphatic amino acid. The methyl group of alanine is non-reactive and is thus almost never directly involved in protein function.
Apr 6, 2011
Amino acids
What are aminoacids?
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. They are particularly important in biochemistry, where the term usually refers to alpha-amino acids.
An alpha-amino acid has the generic formula H2NCHRCOOH, where R is an organic substituent; the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (the α–carbon). Other types of amino acid exist when the amino group is attached to a different carbon atom; for example, in gamma-amino acids (such as gamma-amino-butyric acid) the carbon atom to which the amino group attaches is separated from the carboxylate group by two other carbon atoms. The various alpha-amino acids differ in which side-chain (R-group) is attached to their alpha carbon, and can vary in size from just one hydrogen atom in glycine to a large heterocyclic group in tryptophan.
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. They are particularly important in biochemistry, where the term usually refers to alpha-amino acids.
An alpha-amino acid has the generic formula H2NCHRCOOH, where R is an organic substituent; the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (the α–carbon). Other types of amino acid exist when the amino group is attached to a different carbon atom; for example, in gamma-amino acids (such as gamma-amino-butyric acid) the carbon atom to which the amino group attaches is separated from the carboxylate group by two other carbon atoms. The various alpha-amino acids differ in which side-chain (R-group) is attached to their alpha carbon, and can vary in size from just one hydrogen atom in glycine to a large heterocyclic group in tryptophan.
Mar 31, 2011
Most efficient process ever known to man is Photosynthesis
Most of the science people are familiar with the laws of Thermodynamics.It is stated that "Energy is neither created, nor destroyed ; it can only be transformed from one state to another".For instance, Photosynthesis which converts the light energy into chemical energy.
The another important statement is that "It is impossible to construct an engine, which absorbs heat from a single body and transforms completely to work without losing some energy".For instance, combustion of petroleum products in combustion engines produces energy, which is never completely converted into workdone.It is proven that only an average of 30 to 40 % of energy is only converted to work obtained from combustion of fuels.
Based on this, the efficiency of a machine or a process is calculated given by the ratio of output to the input, multiplied by 100.The output may be the workdone or heat energy released, while the input may be the fuel, which is converted to energy to give the output.It is stated that,"Efficiency of a machine can never be cent percentage" which accompanies the second statement.Any engine with cent % efficiency are said to be perpetual engine, but it is hypothetical.While the most efficient man made process is fermentation whose percentage efficiency is about 57%.No man made engines exceeds the efficiency percentage of 60%.But the thing we can't make is being made by the nature, i.e Photosynthesis.It is scientifically proven that the average efficiency of photosynthesis in common plants is 70%.Let we know how it is.
The another important statement is that "It is impossible to construct an engine, which absorbs heat from a single body and transforms completely to work without losing some energy".For instance, combustion of petroleum products in combustion engines produces energy, which is never completely converted into workdone.It is proven that only an average of 30 to 40 % of energy is only converted to work obtained from combustion of fuels.
Based on this, the efficiency of a machine or a process is calculated given by the ratio of output to the input, multiplied by 100.The output may be the workdone or heat energy released, while the input may be the fuel, which is converted to energy to give the output.It is stated that,"Efficiency of a machine can never be cent percentage" which accompanies the second statement.Any engine with cent % efficiency are said to be perpetual engine, but it is hypothetical.While the most efficient man made process is fermentation whose percentage efficiency is about 57%.No man made engines exceeds the efficiency percentage of 60%.But the thing we can't make is being made by the nature, i.e Photosynthesis.It is scientifically proven that the average efficiency of photosynthesis in common plants is 70%.Let we know how it is.
Mar 15, 2011
Just travelling together can save our planet
Driving a 4 wheeler with 15 mpg economy emits 95 kilogram of Carbon dioxide to the atmosphere for every ten miles.But travelling in a public buses or trains can save a lot.
Mar 9, 2011
Pi
Pi(π) is a mathematical constant, which is the ratio of circumference of the circle to its diameter.
For instance, take a unit circle of diameter as one unit.Then the value of pi will be equal to the circumference of the circle.
Here is the value of pi upto 10000 decimals:
pi=3.14159 26535 89793 23846 26433 83279 50288 41971 69399 37510 58209 74944 59230 78164 06286 20899 86280 34825 34211 70679 82148 08651 32823 06647 09384 46095 50582 23172 53594 08128 48111 74502 84102 70193 85211 05559 64462 29489 54930 38196 44288 10975 66593 34461 28475 64823 37867 83165 27120 19091 45648 56692 34603 48610 45432 66482 13393 60726 02491 41273 72458 70066 06315 58817 48815 20920 96282 92540 91715 36436 78925 90360 01133 05305 48820 46652 13841 46951 94151 16094 33057 27036 57595 91953 09218 61173 81932 61179 31051 18548 07446 23799 62749 56735 18857 52724 89122 79381 83011 94912 98336 73362 44065 66430 86021 39494 63952 24737 19070 21798 60943
For instance, take a unit circle of diameter as one unit.Then the value of pi will be equal to the circumference of the circle.
Here is the value of pi upto 10000 decimals:
pi=3.14159 26535 89793 23846 26433 83279 50288 41971 69399 37510 58209 74944 59230 78164 06286 20899 86280 34825 34211 70679 82148 08651 32823 06647 09384 46095 50582 23172 53594 08128 48111 74502 84102 70193 85211 05559 64462 29489 54930 38196 44288 10975 66593 34461 28475 64823 37867 83165 27120 19091 45648 56692 34603 48610 45432 66482 13393 60726 02491 41273 72458 70066 06315 58817 48815 20920 96282 92540 91715 36436 78925 90360 01133 05305 48820 46652 13841 46951 94151 16094 33057 27036 57595 91953 09218 61173 81932 61179 31051 18548 07446 23799 62749 56735 18857 52724 89122 79381 83011 94912 98336 73362 44065 66430 86021 39494 63952 24737 19070 21798 60943
Mar 8, 2011
The Big bang theory theme
The Big bang theory theme (barenaked ladies):
Lyrics:
Our whole universe was in a hot dense state,
Then nearly fourteen billion years ago expansion started. Wait...
The Earth began to cool,
The autotrophs began to drool,
Neanderthals developed tools,
We built a wall, we built the pyramids,
Math, science, history, unravelling the mysteries,
That all started with the big bang! BANG!
Mar 6, 2011
How to make a smoke bomb?
Ingredients:
- Sugar(sucrose)
- Potassium nitrate which is sold as saltpeter in garden supply stores or sometimes as stump remover
Mix the sugar and Potassium nitrate in the ratio of 2:3 respectively.Now heat the ingredients in a nonstick pan since they melts to form a brownish mixture which may stick to ordinary pans.In ordinary pans hot water may be used to get off the sticky mixture.Once the ingredients melt together, take off from the heat and drop spoonful of the mixture in the foil.Now, it is ready to go out and light up.
Mar 5, 2011
Evolution of sapiens
From Eusthenopteron to Homo sapiens
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)